Social Network Data and Working with Multiple Networks
Dan Cunningham
May 7, 2019
Network Data and Attribute Data
- One-mode relational data - consists of a single set of actors.
- Person-to-person, or user account-to-user account relationships
- Kinship, friendship networks (online and offline)
- Undirected and/or Directed
- Two-mode relational data - consists of two sets of actors.
- Person-to-organization, person-to-event, person-to-evidence, person-to-location
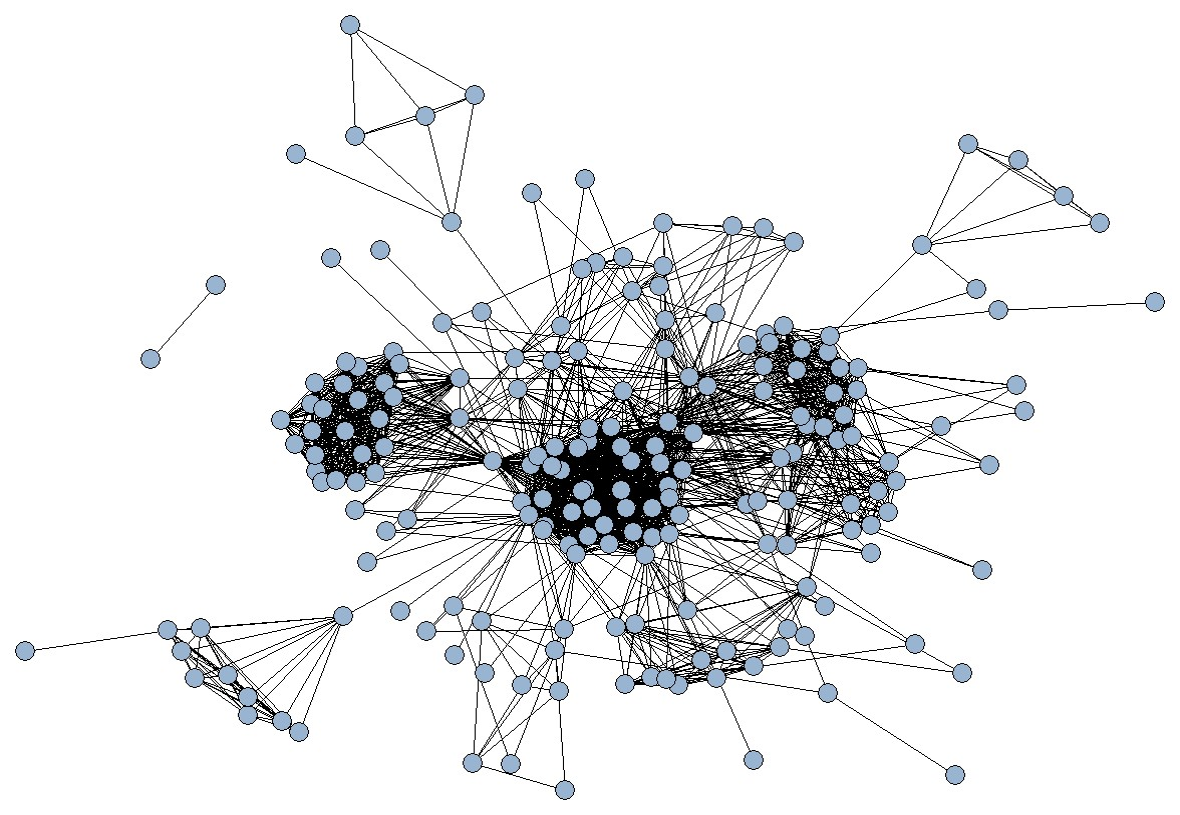
- A two-mode network can be transformed into a one-mode network
- Attribute data - Attributes are non-relational characteristics of the individual actors in the network.
- Individual attributes: gender, race, ethnicity, years of education, income level, age, region/country of birth
- Organizational attributes: total sales, net income, age of the corporation, number of employees/members
What type of network data?
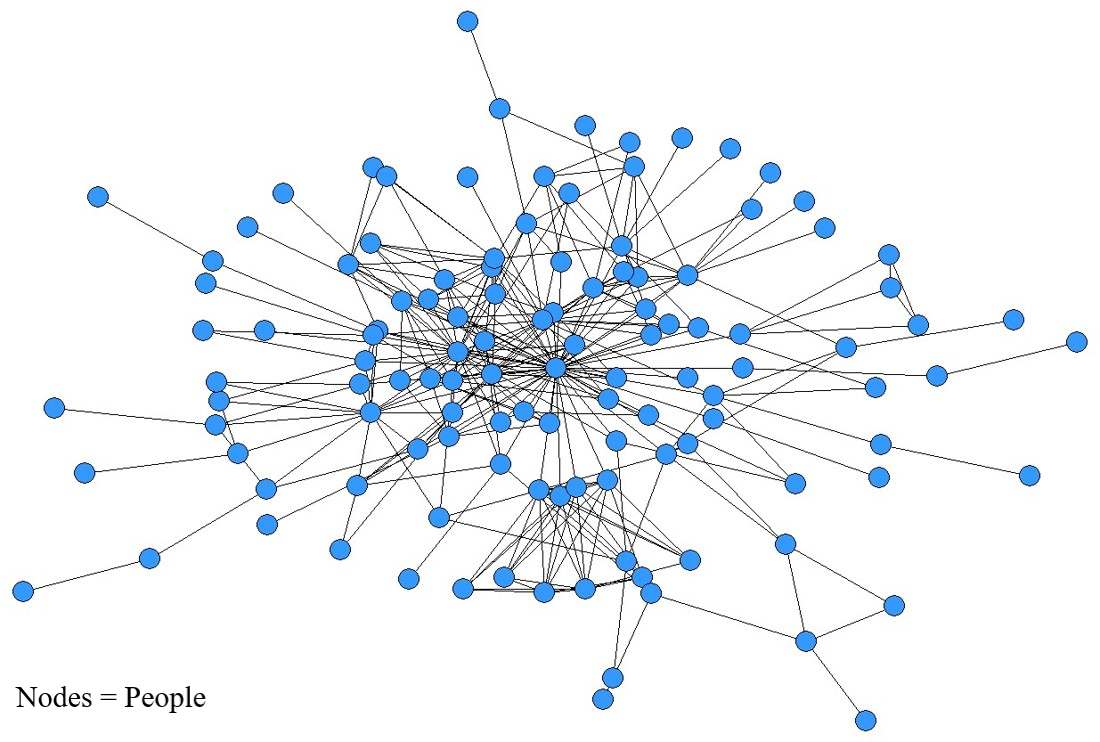
What type of network data?
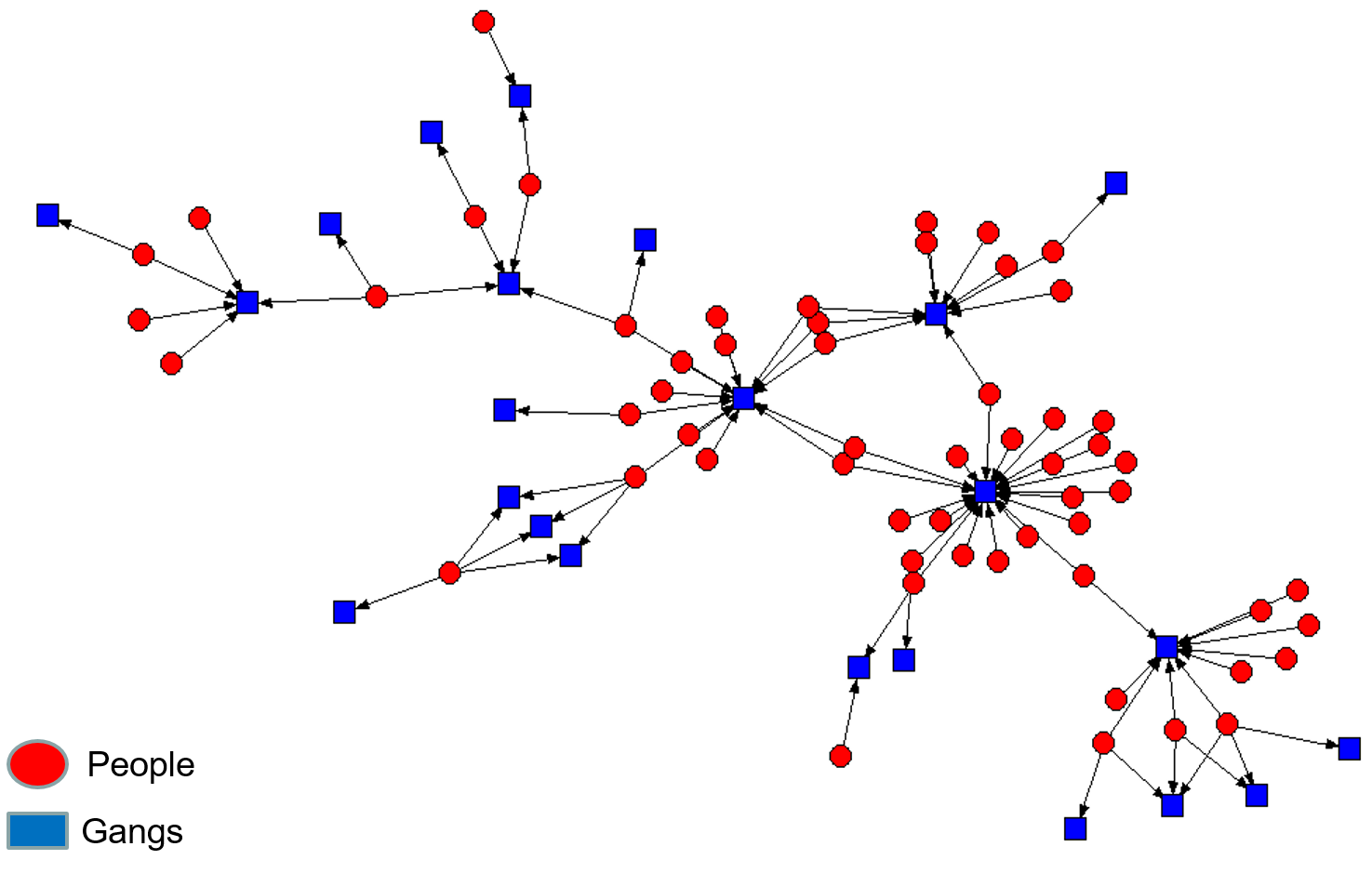
Two-Mode Network
Converted Network (One-Mode)

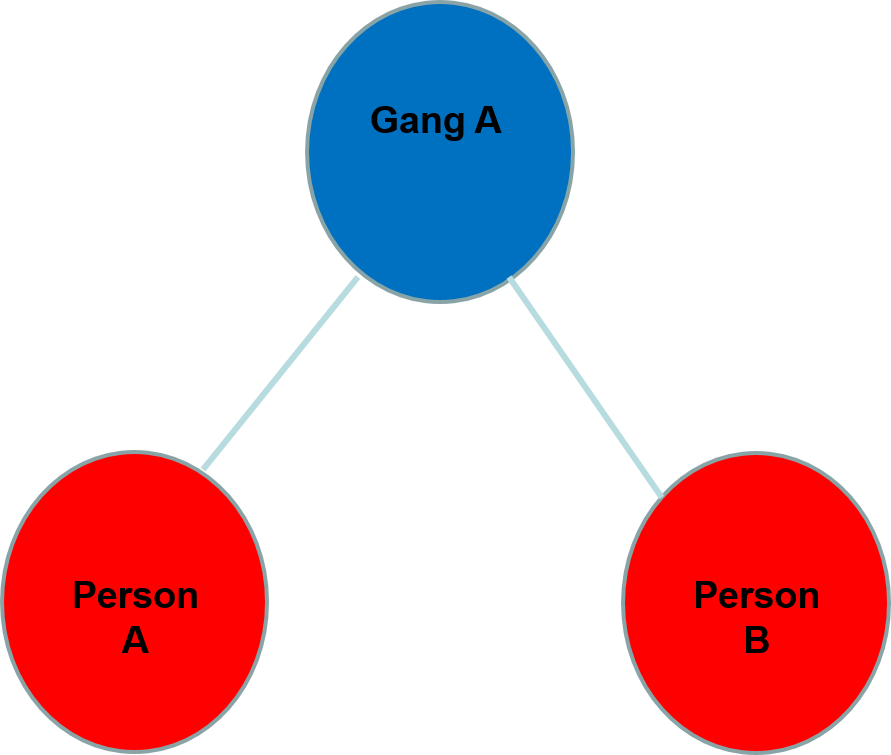
Why do we use attributes in SNA?
Why do we use attributes in SNA?
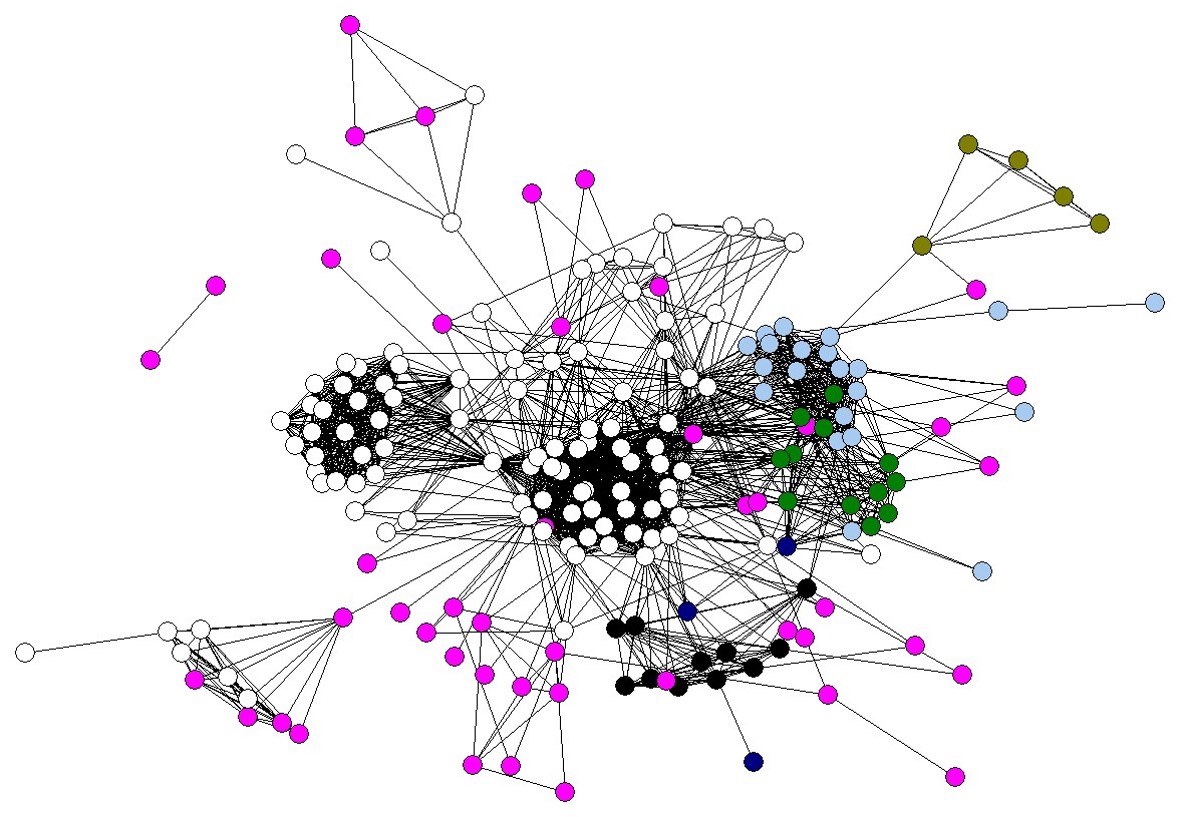
Structured Data
What is structured data?
What are the advantages of structuring data?
How do we structure data?
ORA’s Simple Table
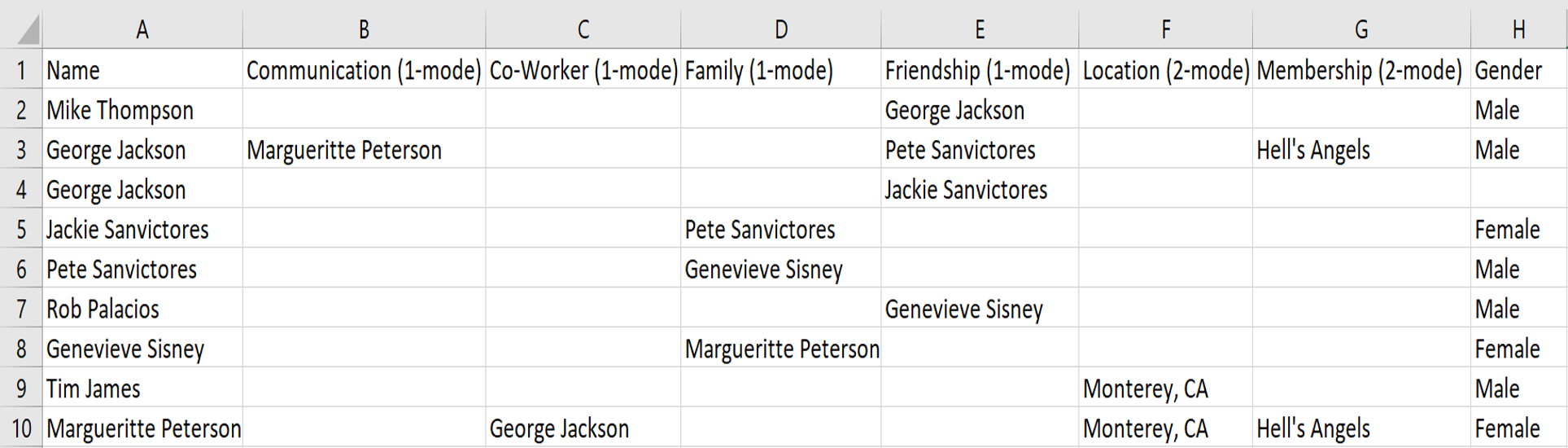
ORA’s Advanced Table
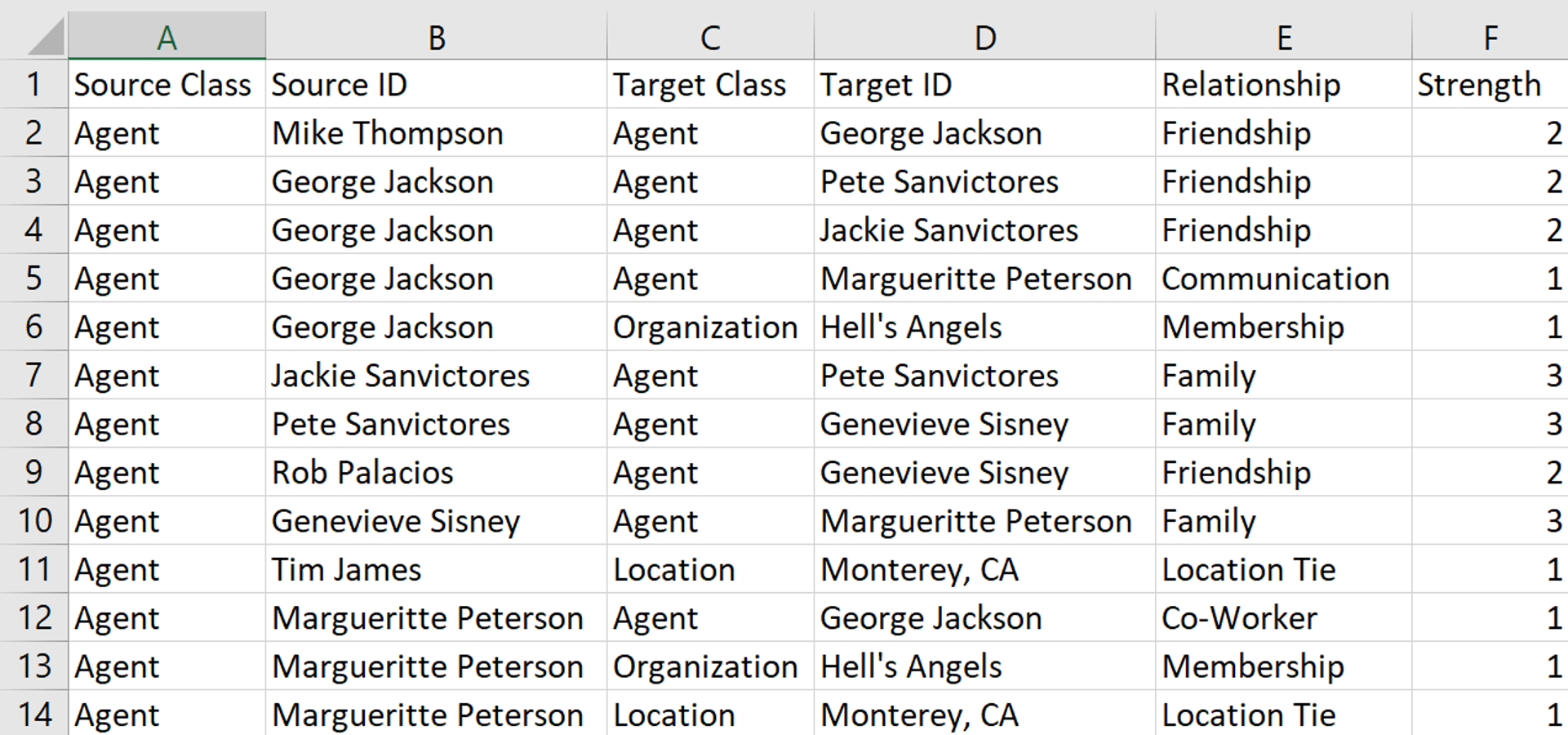
Leveraging Technology for Relational Data
Why do we work with multiple networks?
Actors are typically involved in more than one relation (even with same person).
Different ties often push and pull us in different directions (ties can be at cross-purposes with one another).
Terms
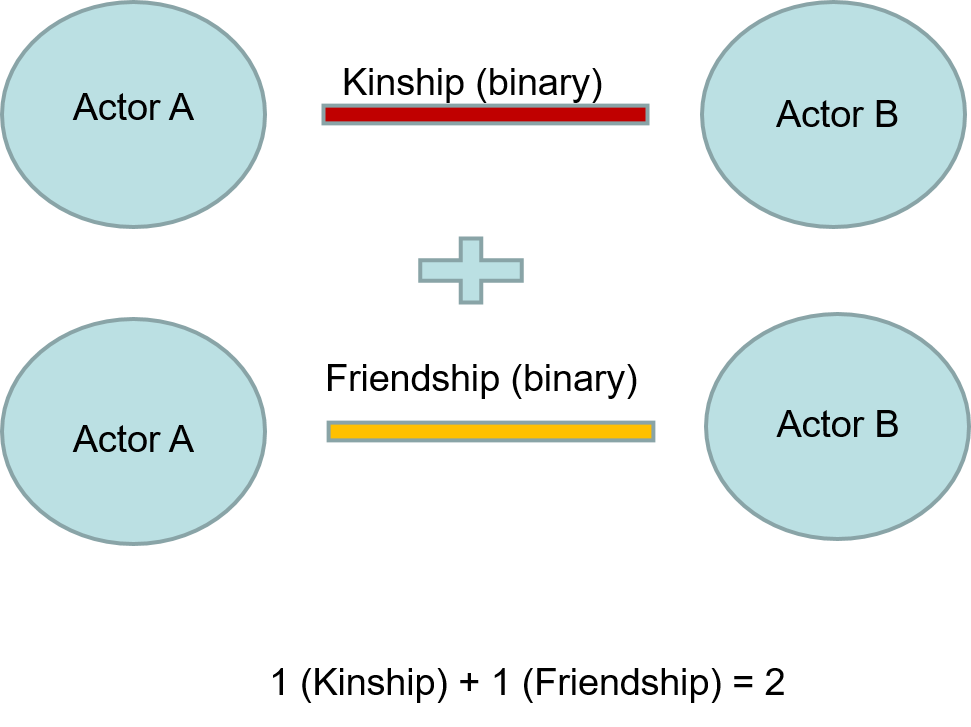
Binary/dichotomous Networks - networks where relational values indicate only the presence or absence of a tie between actors. A tie either exists or it does not (i.e., Yes = 1 or No=0).
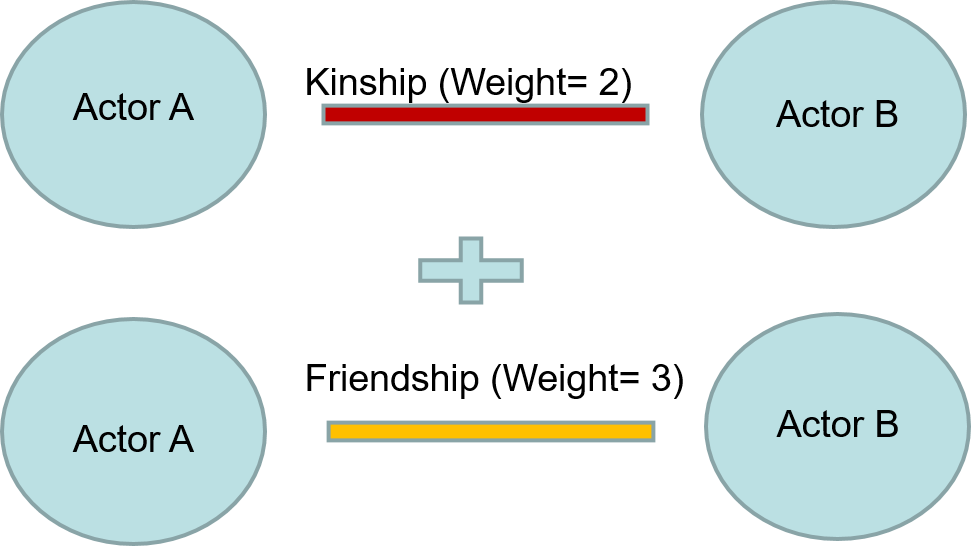
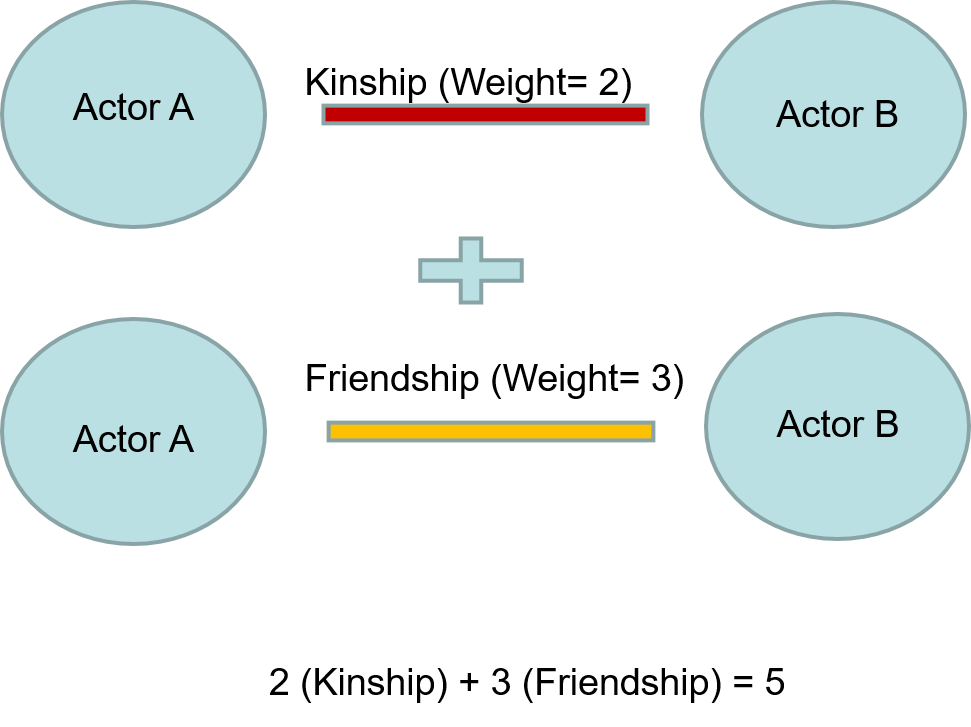
Weighted Networks - networks that contain relationships with a strength or aggregate value.
Knowing this is important when running metrics/statistics.
Binary Example
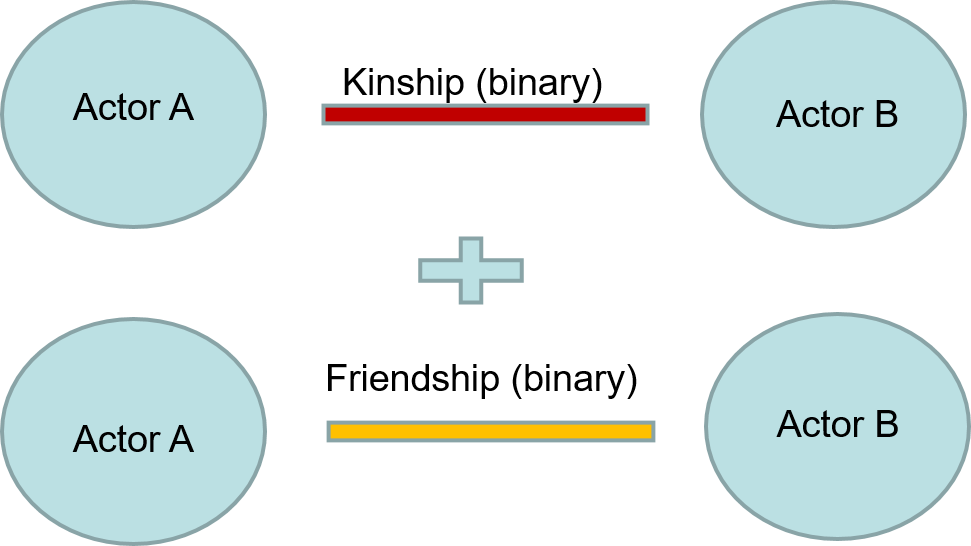
Binary Example
Weighted Example
Weighted Example
Techniques and Data Manipulation
Three Common Techniques
- Three approaches for working with multiple relations:
- Stacking
- Aggregating
- Extraction
Retweets
Mentions
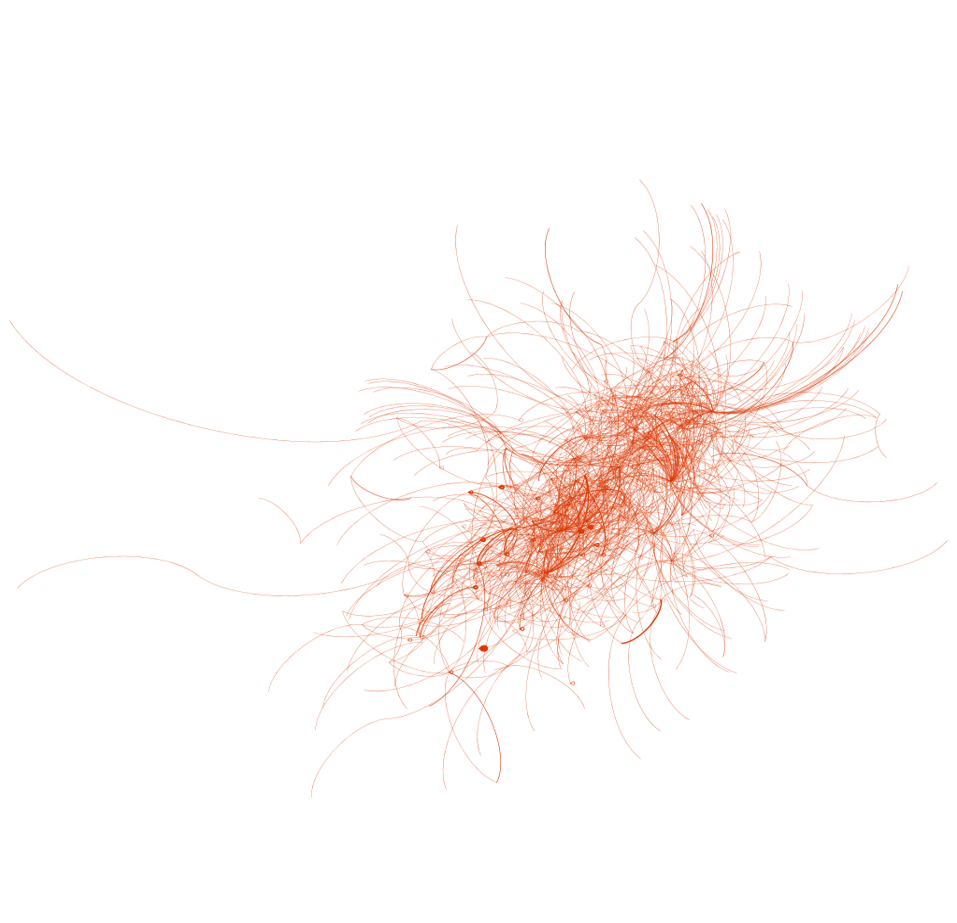
Shared Hashtags
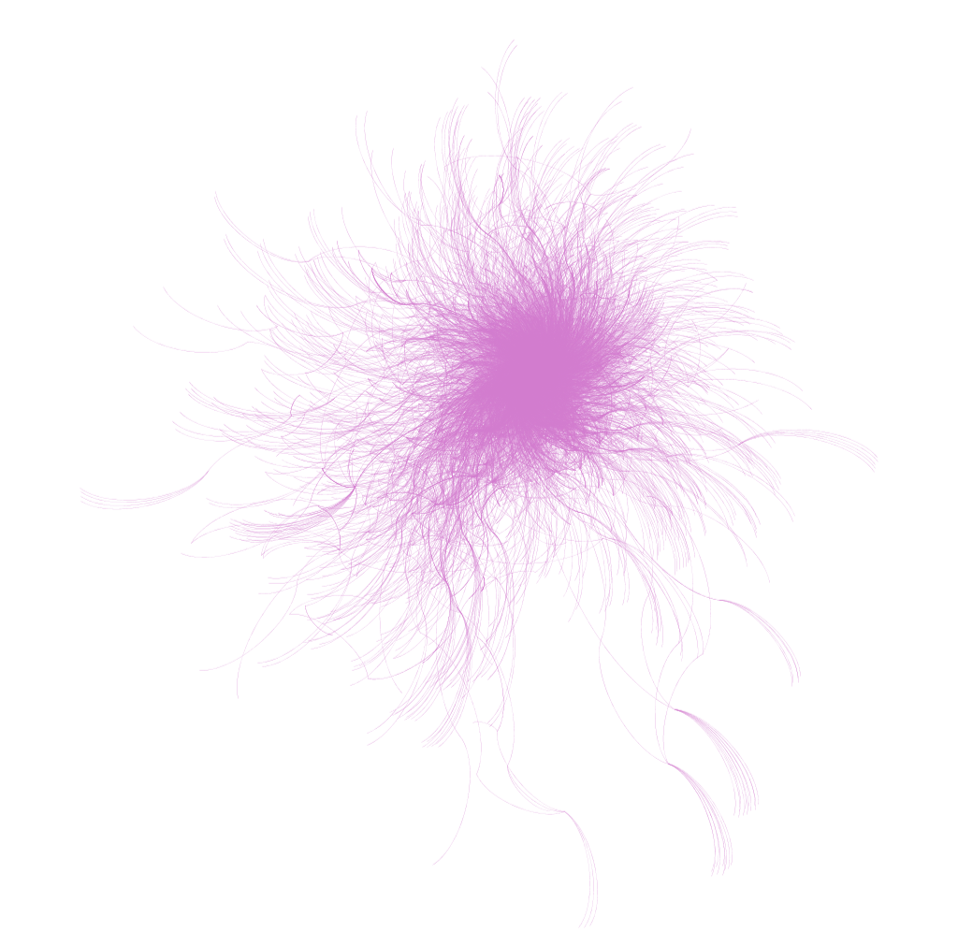

Retweets, Mentions, and Hashtags (Shared)
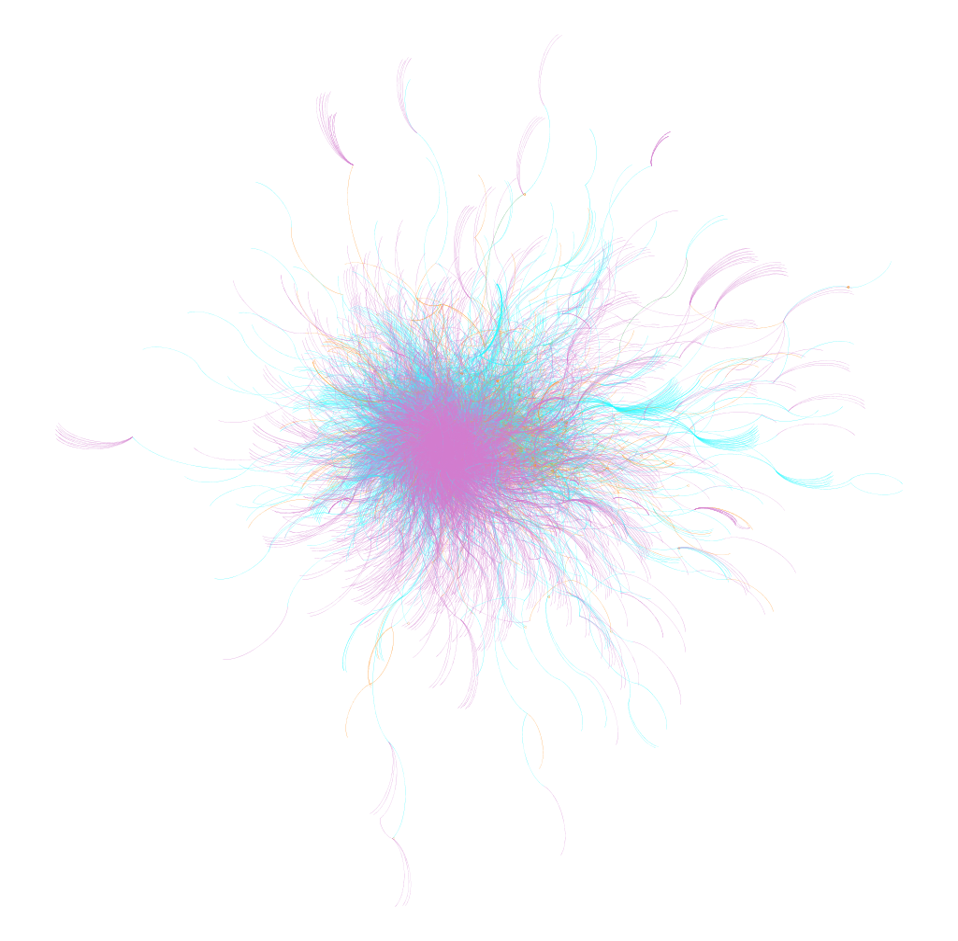

Defining Social Networks
Codebooks
Offline Networks and Data
Coding
Coding is essentially the process of identifying and interpreting information, and subsequently categorizing that information to facilitate data analysis.
Not necessarily the same as data structuring.
Coding
Mike is often seen hanging out with Glenn. The former is a known member of Criminal Group X and the latter is a outspoken member of Criminal Group Y.
- What do we do?
- Identify relevant info (relatively straightforward).
- Interpret the info.
- Categorize the info.
- Structure the info into data.
Coding Example
Actor F Actor F regularly communicates with Actor P, and she infrequently texts with Actor Z. She has been known to hang out with Actors B, L and N (N is a 19-year old male, Group Y Member). She is romantically involved with Actor H and has met Actor B on one occasion. Finally, she was detained with Actor D about 3-months ago.
Coding Example
Actor F Actor F regularly communicates with Actor P, and she infrequently texts with Actor Z. She has been known to hang out with Actors B, L and N (N is a 19-year old male, Group Y Member). She is romantically involved with Actor H and has met Actor B on one occasion. Finally, she was detained with Actor D about 3-months ago.
Relationship Definitions
- Communication: Direct, in-person relaying of messages or information between individuals or through some sort of medium, such as a cellular telephone (e.g., text) or email.
- Friendship: Two people who explicitly acknowledge they are friends or who are seen to associate with one another.
- Co-Event: Two or more people detained with one another.
- Affiliation: An individual’s membership in an organization.
- Romance: Two people who are dating, or involved in an affectionate, romantically-involved relationship.
Codebook

Codebook

Why Codebooks?
- Improves reliability
- Quality of other’s data
- Contextual benefits
- Contributes to better decision-making
Codebooks and Online Data
Questions?

Social Network